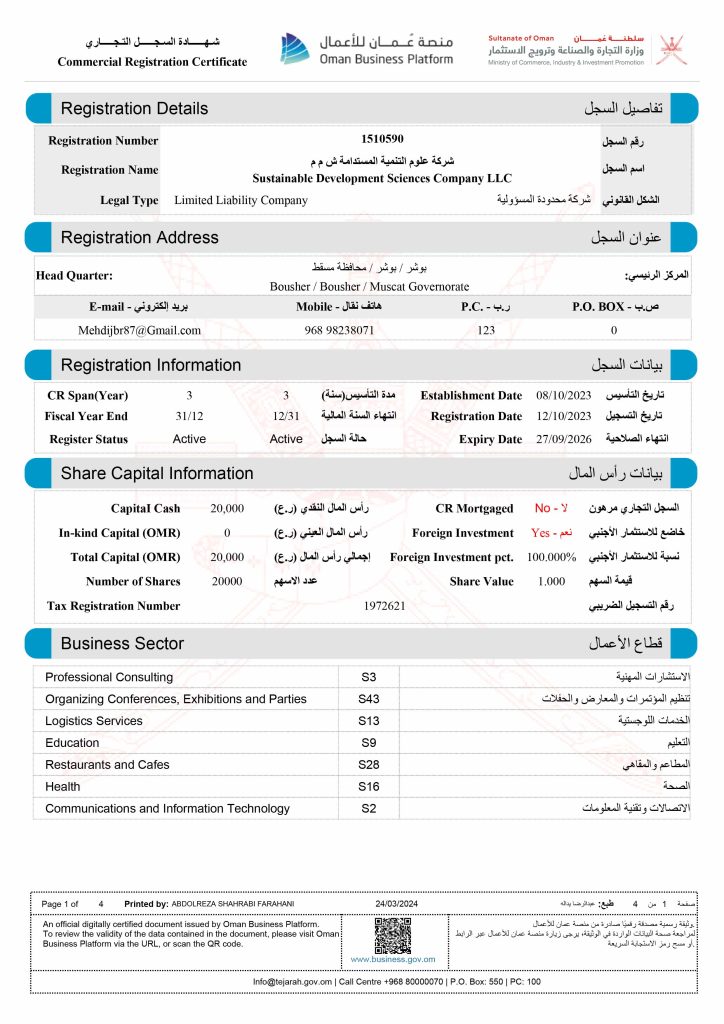
Commercial Registration No: 1510590
Legal Type: LLC
Registration Date: 12/10/2023 – Sultanate of Oman
Business Location: Muscat Governorate / Bousher / Bousher
CR Establishment Date: 08/10/2023
Activity Names:
1- Interdisciplinary Research and Development, Predominantly on Social Sciences and Humanities.
2- Higher Education Services.
3- Scientific Office.
4- Organization of Conventions, Conferences and Meetings.
5- Organization and Operation of Sports Events.
6- Activities of Export and Import Offices.
7- Retail Sale via Internet (E-Commerce).
8- Dental Clinics.
9- Restaurants.
President/Chief Executive Officer: Prof. Abdolreza Shahrabi Farahani
Senior Advisor: Prof. Seyed Vahab Mirsalehi – Philosophy of Thinking and Nietzschean and Grandmaster of Martial Arts
Senior Advisor: Dr. Mohammad Reza Zamani Darmazari – Lawyer and International Law – Human rights and Citizenship rights and Head of the, International Law Commission Human Rights & AT UNESCO MIL APAC
What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development is a concept that refers to a way of utilizing resources and organizing societies in a manner that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves finding a balance between economic development, social progress, and environmental protection. Sustainable development recognizes that our planet has finite resources and that human activities can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. It aims to promote economic growth and improve living standards while ensuring the long-term health of ecosystems and the well-being of all people.
There are three key pillars of sustainable development:
1. Economic Development: This pillar focuses on promoting inclusive economic growth, creating jobs, and ensuring access to essential services and resources. It emphasizes the need for sustainable business practices, innovation, and the efficient use of resources to support long-term economic viability.
2. Social Progress: Sustainable development aims to foster social equity, inclusivity, and justice. It seeks to eradicate poverty, reduce inequality, and improve access to education, healthcare, and basic human rights for all individuals. It also emphasizes the empowerment of marginalized groups and the promotion of social cohesion within communities.
3. Environmental Protection: This pillar recognizes the importance of preserving and restoring the natural environment. It involves managing resources sustainably, minimizing pollution and waste, conserving biodiversity, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. It promotes the use of renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, responsible consumption, and the protection of ecosystems and natural habitats. The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted in 2015, provide a comprehensive framework for global sustainable development efforts. They encompass 17 interconnected goals, including poverty eradication, clean energy, gender equality, sustainable cities, responsible consumption, and climate action, among others. Achieving sustainable development requires collaboration among governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals. It necessitates long-term planning, policy-making, and the adoption of sustainable practices at all levels to ensure a more equitable and environmentally conscious future. Sustainable development in developing societies emphasizes the unique challenges and opportunities faced by these nations as they strive for economic growth, social progress, and environmental sustainability.
Here are some key aspects of sustainable development in developing societies:
1. Poverty Alleviation: Developing societies often have higher levels of poverty, inequality, and limited access to basic services. Sustainable development in these contexts focuses on poverty alleviation through inclusive economic growth, job creation, and social safety nets. It aims to ensure that economic progress benefits all segments of society, particularly the most vulnerable populations.
2. Access to Basic Needs: Sustainable development in developing societies recognizes the importance of providing access to essential needs such as clean water, sanitation, healthcare, education, and energy. Efforts are directed towards improving infrastructure, expanding services, and reducing disparities in access to these fundamental necessities.
3. Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security: Many developing societies are heavily dependent on agriculture for livelihoods and food security. Sustainable development promotes practices that increase agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental degradation. It emphasizes sustainable land management, efficient water use, climate-resilient farming techniques, and support for small-scale farmers to enhance food security and rural development.
4. Renewable Energy and Access to Energy: Developing societies often face challenges in accessing affordable and reliable energy. Sustainable development promotes the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, to meet energy needs while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. It also focuses on expanding energy access in rural areas and promoting energy efficiency to reduce energy poverty and mitigate climate change.
5. Sustainable Urbanization: Rapid urbanization is a common trend in developing societies. Sustainable development seeks to address the associated challenges by promoting sustainable urban planning, efficient transportation systems, affordable housing, access to basic services, and the preservation of green spaces. It aims to create livable, inclusive, and environmentally friendly cities.
6. Environmental Conservation and Climate Action: Developing societies often have rich biodiversity and face environmental threats due to factors like deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Sustainable development encourages the conservation and sustainable management of natural resources, protection of ecosystems and biodiversity, and the adoption of climate change mitigation and adaptation measures.
7. Technology and Innovation: Sustainable development in developing societies recognizes the role of technology and innovation in driving progress. It emphasizes the importance of research and development, technology transfer, and capacity-building to support sustainable practices, enhance productivity, and address specific challenges faced by these societies.
8. Partnerships and International Cooperation: Sustainable development in developing societies requires collaboration between governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector. It involves fostering partnerships to mobilize financial resources, share knowledge and expertise, and support the implementation of sustainable development initiatives. Overall, sustainable development in developing societies seeks to achieve economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental sustainability while addressing the specific challenges and priorities of these nations. It aims to create a future where all individuals can lead dignified lives within the limits of our planet’s resources.
What is Sustainable Development Science?
Sustainable Development Sciences, also known as Sustainability Sciences, is an interdisciplinary field that focuses on understanding and addressing complex sustainability challenges. It combines scientific research, policy analysis, and societal engagement to provide knowledge and solutions for sustainable development. Sustainable Development Sciences recognizes that achieving sustainability requires an integrated approach that considers the interconnections between social, economic, and environmental systems. It seeks to generate evidence-based insights and guide decision-making processes to promote sustainable practices and policies.
Here are some key aspects of Sustainable Development Sciences:
1. Interdisciplinary: Sustainable Development Sciences brings together expertise from various disciplines, including environmental science, ecology, economics, sociology, political science, and engineering. It recognizes that complex sustainability challenges require a holistic understanding that goes beyond traditional disciplinary boundaries.
2. Systems Thinking: Sustainable Development Sciences adopts a systems approach, considering the interactions and feedback loops between different components of social-ecological systems. It examines the interdependencies between human activities, institutions, ecosystems, and the impacts on sustainability outcomes.
3. Research and Analysis: Sustainable Development Sciences conducts research and analysis to deepen our understanding of sustainability issues. It investigates the drivers and consequences of unsustainable practices, assesses the effectiveness of policies and interventions, and explores alternative pathways for sustainable development. This research often involves quantitative modeling, data analysis, scenario planning, and participatory approaches.
4. Policy and Decision Support: Sustainable Development Sciences aims to inform policy-making and decision-making processes. It provides evidence-based recommendations and tools for policymakers, stakeholders, and practitioners to design and implement sustainable policies and practices at various scales—from local to global. It emphasizes the integration of scientific knowledge with local context and stakeholder perspectives.
5. Transdisciplinary Collaboration: Sustainable Development Sciences emphasizes collaboration among researchers, policymakers, practitioners, and communities. It actively engages stakeholders from diverse sectors and backgrounds to ensure that scientific knowledge is relevant, actionable, and inclusive.
6. Sustainability Goals and Indicators: Sustainable Development Sciences often aligns with global frameworks, such as the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It contributes to the development and refinement of indicators and metrics to measure progress towards sustainability goals. This includes tracking indicators related to poverty, inequality, climate change, biodiversity, resource use, and other dimensions of sustainability.
7. Innovation and Solutions: Sustainable Development Sciences seeks to identify and develop innovative solutions for sustainability challenges. It explores technological innovations, policy instruments, governance approaches, social innovations, and behavioral changes that can contribute to sustainable development.
8. Education and Capacity-building: Sustainable Development Sciences plays a role in educating and building capacity among future generations of researchers, policymakers, and practitioners. It promotes interdisciplinary education, fosters critical thinking, and encourages collaboration across disciplines to address sustainability challenges effectively. By integrating scientific knowledge, policy analysis, and societal engagement, Sustainable Development Science aims to advance our understanding of sustainability challenges and contribute to the transition towards a more sustainable and equitable future.
What is the role of “Philosophy” in Sustainable Development Sciences?
Philosophy plays a crucial role in sustainable development sciences by providing a framework for critical reflection, ethical inquiry, and conceptual analysis.
Here are some key roles that philosophy can play in the field:
1. Ethical Reflection: Sustainable development involves making choices that balance the needs of present and future generations, as well as the well-being of humans and the environment. Philosophy contributes to sustainable development sciences by engaging in ethical reflection and analysis. It explores different ethical theories, such as consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics, to examine the moral foundations and implications of sustainable development practices and policies. Philosophical inquiry helps to identify and address ethical dilemmas, conflicts of interest, and value trade-offs in decision-making processes.
2. Conceptual Clarity: Sustainable development encompasses complex and interconnected concepts. Philosophy helps to clarify and refine these concepts by analyzing their meanings, assumptions, and implications. It engages in conceptual analysis to provide clearer definitions and distinctions, ensuring a more precise understanding and communication within the field of sustainable development sciences. Philosophical inquiry can shed light on concepts such as sustainability, justice, well-being, resilience, and responsibility, enabling more effective discourse and interdisciplinary collaboration.
3. Epistemological Inquiry: Philosophy engages in critical examination of knowledge, truth, and the nature of scientific inquiry. Within sustainable development sciences, philosophical inquiry can reflect on the epistemological foundations of different research approaches, methodologies, and paradigms. It encourages a critical examination of the assumptions, limitations, and biases within scientific knowledge production. By fostering epistemological inquiry, philosophy helps ensure the rigor, objectivity, and reflexivity of scientific practice in sustainable development.
4. Normative Frameworks: Sustainable development sciences require normative frameworks to guide decision-making and action. Philosophy provides tools for developing such frameworks by examining different ethical theories, political philosophies, and value systems. It contributes to the construction of normative frameworks that can inform and guide sustainable development policies, practices, and governance arrangements. Philosophy helps to explore questions of distributive justice, human rights, intergenerational equity, and the responsibilities of individuals, institutions, and governments in achieving sustainable development goals.
5. Critical Thinking and Reflexivity: Philosophy promotes critical thinking and reflexivity within sustainable development sciences. It encourages researchers and practitioners to question assumptions, challenge prevailing paradigms, and engage in self-reflection. Philosophical inquiry helps to uncover underlying assumptions, biases, and power dynamics that may influence sustainable development practices and policies. It fosters a critical examination of dominant narratives, ideologies, and interests, thereby enabling more informed and nuanced approaches to sustainable development challenges.
6. Interdisciplinary Integration: Sustainable development sciences are inherently interdisciplinary, addressing complex social, economic, and environmental issues. Philosophy, as a discipline that bridges various fields of inquiry, facilitates interdisciplinary integration. It encourages dialogue and collaboration between different disciplines, helping to synthesize diverse perspectives, methods, and insights. Philosophical inquiry can foster a holistic understanding of sustainability challenges, recognizing the interdependencies and complex relationships between different systems. By engaging in ethical reflection, conceptual analysis, normative inquiry, and critical thinking, philosophy enriches the field of sustainable development sciences. It provides a broader perspective and deeper understanding of the ethical, social, and philosophical dimensions of sustainability, contributing to the development of more comprehensive and ethically grounded approaches to sustainable development.
What is the role of social sciences and humanities in Sustainable Development Sciences?
Social sciences and humanities play a crucial role in Sustainable Development Sciences by providing insights into human behavior, societal dynamics, cultural values, and policy analysis. They contribute to understanding the social, economic, and political dimensions of sustainability challenges and help shape effective and contextually relevant solutions.
Here are some key roles of social sciences and humanities in Sustainable Development Sciences:
1. Understanding Human Behavior: Social sciences, such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and economics, help to understand human behavior and decision-making processes concerning sustainable development. They examine individual and collective behaviors, social norms, cultural values, and attitudes towards sustainability issues. This understanding is essential for designing interventions, policies, and communication strategies that can promote sustainable practices and behavior change.
2. Assessing Social Impacts: Social sciences provide tools and methodologies to assess the social impacts of sustainable development initiatives. They examine the distributional effects, social inequalities, and social justice implications of policies and interventions. Social impact assessments help ensure that sustainable development initiatives consider the needs and aspirations of different social groups, address inequalities, and promote inclusive development.
3. Policy Analysis and Governance: Social sciences contribute to policy analysis and governance research within sustainable development sciences. They examine the effectiveness of policies, institutions, and governance arrangements in achieving sustainability goals. Social scientists analyze policy processes, stakeholder engagement, decision-making structures, and power dynamics to identify opportunities for more inclusive and participatory governance frameworks that can drive sustainable development.
4. Cultural Context and Values: Humanities and cultural studies provide insights into the cultural dimensions of sustainable development. They explore the relationships between culture, identity, and sustainability, and how cultural values, practices, and narratives shape human-environment interactions. Understanding cultural contexts is crucial for designing culturally appropriate and contextually relevant sustainable development interventions, promoting local knowledge systems, and fostering cultural diversity.
5. Stakeholder Engagement and Participation: Social sciences and humanities emphasize stakeholder engagement and participatory approaches within sustainable development sciences. They provide methodologies for involving diverse stakeholders, including local communities, indigenous peoples, civil society organizations, and marginalized groups, in decision-making processes. These approaches ensure that sustainable development initiatives are informed by local knowledge, experiences, and aspirations, enhancing their legitimacy and effectiveness.
6. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Social sciences and humanities facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration within sustainable development sciences. They bridge natural sciences, engineering, economics, and policy studies with insights from sociology, anthropology, geography, history, philosophy, and other disciplines. This collaboration helps integrate diverse perspectives, knowledge, and methods, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of sustainability challenges and opening avenues for innovative solutions.
7. Communication and Public Engagement: Social sciences and humanities contribute to effective communication and public engagement in sustainable development. They provide tools and approaches for science communication, public perception analysis, and the use of narratives and storytelling to convey complex sustainability issues to diverse audiences. Social scientists and humanities scholars play a vital role in translating scientific findings into accessible and relatable information, fostering public awareness, and facilitating informed public debates. By integrating social sciences and humanities, Sustainable Development Sciences gain a deeper understanding of the social, cultural, economic, and political dimensions of sustainable development. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that sustainability strategies are contextually relevant, socially just, and inclusive, leading to more effective and equitable solutions to sustainability challenges.
How can the role of Sustainable Development Sciences Company be in the Sultanate of Oman?
A Sustainable Development Sciences Company in the Sultanate of Oman can play a significant role in advancing sustainable development goals and promoting sustainable practices in various sectors.
Here are some potential roles and contributions such a company can have:
1. Research and Analysis: The company can conduct research and analysis on sustainability issues specific to Oman, such as renewable energy, water management, waste management, biodiversity conservation, and climate change adaptation. It can provide data-driven insights and scientific evidence to inform policy-making, investment decisions, and sustainable development strategies in the country.
2. Solutions and Innovations: The company can develop and implement innovative solutions to address sustainability challenges in Oman. It can work on developing sustainable technologies, energy-efficient solutions, circular economy practices, and nature-based solutions tailored to the local context. These innovations can contribute to resource efficiency, reduced carbon emissions, and improved environmental performance across sectors.
3. Policy Support and Consultancy: A Sustainable Development Sciences Company can offer policy support and consultancy services to government agencies, businesses, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). It can assist in the development and implementation of sustainable development policies, guidelines, and action plans. The company can provide expertise on regulatory frameworks, best practices, and international standards to promote sustainable development in Oman.
4. Capacity Building and Training: The company can contribute to capacity building efforts by providing training programs, workshops, and educational initiatives on sustainable development topics. It can enhance the knowledge and skills of government officials, professionals, and community members in areas such as sustainable resource management, environmental conservation, climate change mitigation, and social responsibility.
5. Sustainable Business Practices: The Sustainable Development Sciences Company can support businesses in adopting sustainable practices and integrating sustainability into their operations. It can offer sustainability assessments, auditing services, and guidance on sustainable supply chains, corporate social responsibility, and green finance. The company can assist businesses in achieving sustainability certifications and labels to enhance their environmental and social performance.
6. Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration: The company can facilitate stakeholder engagement and collaboration among various actors in Oman’s sustainable development landscape. It can bring together government agencies, businesses, NGOs, research institutions, and local communities to foster dialogue, knowledge sharing, and joint initiatives. The company can act as a platform for partnerships and collaborations to drive collective action towards sustainable development goals.
7. Awareness and Communication: An important role of the company would be to raise awareness about sustainable development issues and promote a culture of sustainability in Oman. It can develop communication campaigns, educational materials, and public outreach initiatives to engage and inform the public about the importance of sustainable practices and their benefits. The company can also leverage digital platforms and social media to disseminate information and encourage behavior change. Overall, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company in the Sultanate of Oman can contribute to sustainable development by providing research, solutions, policy support, capacity building, and stakeholder engagement. By working closely with stakeholders and promoting sustainable practices, the company can help Oman move towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Interdisciplinary Research and Development, Predominantly on Social Sciences and Humanities:
The objectives of conducting interdisciplinary research and development, predominantly focused on social sciences and humanities, within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Comprehensive Understanding: The objective is to develop a comprehensive understanding of sustainable development by integrating social sciences and humanities perspectives. This interdisciplinary approach recognizes the interconnections between social, cultural, economic, and environmental dimensions of sustainability. It aims to unravel complex relationships, dynamics, and feedback loops to provide a more holistic understanding of sustainability challenges.
2. Contextual Analysis: The objective is to analyze the social, cultural, and human factors that influence sustainable development outcomes. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can provide insights into the social and cultural contexts in which sustainable development policies and interventions are implemented. It aims to understand societal values, cultural practices, historical legacies, and power dynamics that shape sustainability outcomes in specific contexts.
3. Policy and Governance: The objective is to contribute to evidence-based policy-making and governance processes in sustainable development. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can generate knowledge and insights that inform the development and implementation of sustainable development policies, strategies, and frameworks. It aims to provide policymakers with a deeper understanding of social and cultural barriers, opportunities, and trade-offs associated with sustainability initiatives.
4. Social Equity and Justice: The objective is to address social equity and justice concerns in sustainable development. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can explore issues of social inequality, gender equity, human rights, and marginalized populations within the context of sustainable development. It aims to identify strategies and approaches to ensure that sustainable development initiatives are inclusive, equitable, and promote social justice.
5. Behavior Change and Participation: The objective is to understand human behavior and promote sustainable practices and behaviors. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can examine factors that influence individual and collective behavior change towards sustainability. It aims to develop effective strategies for promoting sustainable lifestyles, citizen participation, and community engagement in sustainable development initiatives.
6. Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration: The objective is to engage diverse stakeholders in sustainable development research and practice. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can facilitate stakeholder engagement and collaboration among academia, government agencies, civil society organizations, and local communities. It aims to create spaces for dialogue, knowledge exchange, and co-creation of solutions, ensuring that diverse perspectives and voices are included in sustainable development processes.
7. Communication and Public Awareness: The objective is to effectively communicate research findings and raise public awareness about sustainable development issues. Interdisciplinary research in social sciences and humanities can employ accessible and engaging communication strategies to disseminate research outcomes to policymakers, practitioners, and the general public. It aims to bridge the gap between research and practice, foster informed public discourse, and promote behavior change towards sustainability. By pursuing these objectives, interdisciplinary research and development in social sciences and humanities within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company contribute to a deeper understanding of the social, cultural, and human dimensions of sustainable development. It informs policy-making processes, promotes social equity and justice, facilitates behavior change, and enhances stakeholder engagement and collaboration in sustainable development initiatives.
Higher Education Services:
The objectives of providing “Higher Education Services” in the context of a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Knowledge and Skill Development: The objective is to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and competencies necessary to contribute effectively to sustainable development. Higher education services aim to provide comprehensive and interdisciplinary education in sustainable development sciences, including social sciences, humanities, natural sciences, and engineering. This education helps students understand the complex challenges of sustainability and develop innovative and sustainable solutions.
2. Capacity Building: The objective is to build the capacity of individuals and institutions in sustainable development practices. Higher education services can offer training programs, workshops, and courses that enhance the capacity of professionals, policymakers, and practitioners to integrate sustainability principles into their work. This includes training on sustainable resource management, environmental conservation, climate change mitigation and adaptation, social responsibility, and sustainable business practices.
3. Research and Innovation: The objective is to foster research and innovation in sustainable development sciences. Higher education services can provide opportunities for students and faculty members to engage in research projects that address pressing sustainability challenges. This objective promotes the generation of new knowledge, innovative solutions, and evidence-based approaches to sustainable development. It also encourages collaboration between academia, industry, and other stakeholders to drive sustainable innovation.
4. Partnerships and Collaboration: The objective is to foster partnerships and collaboration between higher education institutions, government agencies, businesses, and civil society organizations in the field of sustainable development. Higher education services can facilitate collaborative research projects, joint initiatives, and knowledge exchange platforms. These partnerships enhance the relevance of higher education to real-world sustainability issues and foster a multidisciplinary and multi-stakeholder approach to addressing sustainability challenges.
5. Knowledge Dissemination: The objective is to disseminate knowledge and research findings on sustainable development to a wider audience. Higher education services can facilitate the sharing of research outcomes, best practices, and innovative approaches through publications, conferences, seminars, and other knowledge-sharing platforms. This objective aims to bridge the gap between academia and society, ensuring that research findings and expertise are accessible and contribute to sustainable development decision-making processes.
6. Ethical and Values-Based Education: The objective is to provide an education that promotes ethical and values-based approaches to sustainable development. Higher education services can integrate ethical considerations, social justice perspectives, and cultural sensitivity into the curriculum. This objective aims to cultivate a sense of responsibility, empathy, and global citizenship among students, fostering a commitment to sustainable and equitable development.
7. Leadership and Change Agents: The objective is to develop future leaders and change agents in sustainable development. Higher education services aim to nurture a new generation of professionals who can drive transformative change towards sustainability in various sectors. This objective focuses on developing leadership skills, critical thinking, and the ability to mobilize and influence others to create positive change. By pursuing these objectives, Higher Education Services within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company contribute to building human capital, fostering innovation, and promoting sustainable practices. They play a crucial role in preparing individuals to address complex sustainability challenges and create a more sustainable and inclusive future.
Scientific Office:
The objectives of the Scientific Office within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Research Coordination: The objective is to coordinate and facilitate research activities related to sustainable development. The Scientific Office plays a crucial role in identifying research priorities, developing research plans, and coordinating research projects within the company. It ensures that research efforts are aligned with the company’s overall goals and objectives in sustainable development.
2. Knowledge Management: The objective is to effectively manage and disseminate knowledge generated through research activities. The Scientific Office oversees the collection, organization, and analysis of research data, findings, and publications. It establishes systems and platforms for knowledge sharing and ensures that research outcomes are accessible to relevant stakeholders, including policymakers, practitioners, and the public.
3. Collaborative Partnerships: The objective is to foster collaborative partnerships with external research institutions, universities, and other stakeholders in the field of sustainable development. The Scientific Office facilitates the establishment of research collaborations, joint projects, and knowledge exchange initiatives. It aims to leverage external expertise and resources to enhance the research capabilities and impact of the company.
4. Quality Assurance: The objective is to ensure the quality and rigor of research conducted within the company. The Scientific Office establishes and implements quality assurance processes, including research methodologies, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It promotes adherence to ethical standards and best practices in research, ensuring the reliability and validity of research findings.
5. Innovation and Technology Integration: The objective is to promote innovation and the integration of emerging technologies in sustainable development research. The Scientific Office identifies opportunities to leverage new technologies, such as data analytics, remote sensing, artificial intelligence, and modeling tools, to enhance research capabilities and generate innovative solutions to sustainability challenges.
6. Policy Support: The objective is to provide scientific and technical support to inform policy-making processes in sustainable development. The Scientific Office translates research findings into actionable insights and policy recommendations. It collaborates with policymakers and stakeholders to ensure that research outcomes are effectively integrated into policy development, implementation, and evaluation processes.
7. Capacity Building: The objective is to build the research capacity of the company’s staff members and researchers. The Scientific Office identifies training needs, organizes capacity-building activities, and promotes professional development opportunities in sustainable development research methodologies, data analysis techniques, and interdisciplinary approaches. It aims to enhance the expertise and skills of the research team, enabling them to conduct high-quality research and contribute to sustainable development knowledge. By pursuing these objectives, the Scientific Office within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company plays a vital role in coordinating research efforts, managing knowledge, fostering collaborations, ensuring research quality, supporting policy development, promoting innovation, and building research capacity. It strengthens the company’s research capabilities and contributes to evidence-based decision-making processes in sustainable development.
Organization of Conventions, Conferences and Meetings:
The objectives of organizing conventions, conferences, and meetings within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Knowledge Exchange: The objective is to facilitate the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and best practices in the field of sustainable development. Conventions, conferences, and meetings provide platforms for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders to share their experiences, research findings, and innovative solutions. They foster dialogue, debate, and collaboration, enhancing the collective understanding of sustainable development challenges and opportunities.
2. Networking and Collaboration: The objective is to facilitate networking and collaboration among individuals and organizations working in sustainable development. These events bring together a diverse range of participants, including researchers, policymakers, industry representatives, and civil society organizations. They create opportunities for networking, establishing partnerships, and fostering collaborations that can lead to joint research projects, knowledge exchange, and collective action towards sustainable development goals.
3. Dissemination of Research: The objective is to disseminate research findings and promote academic and scientific discourse. Conventions, conferences, and meetings provide a platform for researchers to present their work through presentations, posters, and panel discussions. They enable researchers to receive feedback, engage in scholarly discussions, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in sustainable development sciences.
4. Policy Influence: The objective is to influence policy-making processes and decision-makers in the field of sustainable development. Conventions, conferences, and meetings often attract policymakers, government officials, and international organizations. They provide opportunities for researchers and practitioners to present evidence-based research and policy recommendations, fostering dialogue and influencing policy agendas towards more sustainable and inclusive development.
5. Capacity Building: The objective is to enhance knowledge and skills among participants related to sustainable development. Conventions, conferences, and meetings can include workshops, training sessions, and capacity-building activities that address emerging issues, methodologies, and tools in sustainable development. They provide a platform for participants to learn from experts, acquire new skills, and enhance their professional development.
6. Public Awareness and Engagement: The objective is to raise public awareness and engage the general public in sustainable development issues. Conventions, conferences, and meetings often include public sessions, exhibitions, and outreach activities that aim to disseminate knowledge, communicate research findings, and engage with the broader community. They contribute to building public support and understanding of sustainable development goals and encourage individual and collective action towards sustainability.
7. International Cooperation: The objective is to foster international cooperation and collaboration in sustainable development. Conventions, conferences, and meetings attract participants from different countries and regions, providing opportunities for cross-border collaboration, knowledge exchange, and sharing of best practices. They facilitate the development of global networks and partnerships that can address transboundary sustainability challenges and promote international cooperation. By organizing conventions, conferences, and meetings, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company achieves objectives such as knowledge exchange, networking, research dissemination, policy influence, capacity building, public engagement, and international cooperation. These activities contribute to advancing the field of sustainable development, fostering collaboration, and driving positive change towards a more sustainable and equitable future.
Organization and Operation of Sports Events:
The objectives of organizing and operating sports events within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Promoting Sustainable Practices: The objective is to promote sustainable practices in sports events. The company aims to organize events that minimize their environmental impact, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, promoting recycling, and using environmentally friendly materials. By implementing sustainable practices, the company sets an example for the sports industry and promotes the integration of sustainability principles in event management.
2. Raising Awareness: The objective is to raise awareness about sustainable development among participants, spectators, and the general public attending sports events. The company utilizes the platform of sports events to educate and engage attendees on sustainability issues, such as climate change, biodiversity conservation, and social responsibility. It aims to inspire behavior change and encourage individuals to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
3. Showcasing Innovation: The objective is to showcase innovative solutions and technologies that contribute to sustainable development. The company uses sports events as a platform to highlight sustainable innovations in areas such as renewable energy, waste management, and eco-friendly transportation. By showcasing these innovations, it promotes their adoption in other sectors and fosters a culture of innovation for sustainability.
4. Community Engagement: The objective is to engage and benefit local communities through sports events. The company seeks to involve local stakeholders, such as community organizations, schools, and businesses, in the planning and execution of events. It aims to create opportunities for community participation, skill development, and economic benefits, thereby leaving a positive social impact on the host communities.
5. Social Inclusion: The objective is to promote social inclusion and diversity within sports events. The company strives to ensure equal opportunities for participation and access to sports events for individuals from different backgrounds, abilities, and socioeconomic statuses. By fostering inclusivity, it aims to promote social cohesion, reduce inequalities, and create a sense of belonging among participants and spectators.
6. Research and Monitoring: The objective is to conduct research and monitoring during sports events to generate knowledge and insights on sustainable development. The company may collect data on energy consumption, waste generation, and participant behavior to assess the environmental and social impact of the events. This research helps in identifying areas for improvement, measuring progress, and informing future event planning.
7. Collaboration and Partnerships: The objective is to collaborate with stakeholders from the sports industry, academia, and civil society to promote sustainable sports events. The company seeks partnerships with organizations and institutions that share its commitment to sustainable development. By working together, they can leverage expertise, resources, and networks to advance sustainable practices in sports event management and foster collective action for sustainability. By organizing and operating sports events with a focus on sustainability, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company aims to promote sustainable practices, raise awareness, showcase innovation, engage communities, foster social inclusion, conduct research, and collaborate with stakeholders. These objectives contribute to the broader goal of integrating sustainable development principles into the sports industry and harnessing its potential to drive positive change for a more sustainable future.
Activities of Export and Import Offices:
The objectives of the Export and Import Offices within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Sustainable Trade: The objective is to promote sustainable trade practices in the import and export activities of the company. The offices aim to ensure that the goods and products being imported or exported align with principles of sustainability, such as environmentally friendly production methods, fair trade practices, and adherence to social and labor standards. They seek to minimize the negative environmental and social impacts associated with international trade.
2. Market Expansion: The objective is to expand the market for sustainable products and technologies through import and export activities. The Export and Import Offices identify sustainable products and technologies that align with the company’s mission in sustainable development. They work to establish market connections, develop distribution networks, and promote the export of sustainable products to new markets. Similarly, they explore opportunities to import sustainable products and technologies that can contribute to the company’s sustainability goals.
3. Knowledge Transfer: The objective is to facilitate knowledge transfer and technology exchange through import and export activities. The Export and Import Offices seek to introduce innovative sustainable technologies and practices to new markets through imports. They also aim to export sustainable technologies, knowledge, and expertise developed within the company to contribute to sustainable development efforts in other countries. The offices act as conduits for knowledge exchange, fostering learning and collaboration across borders.
4. Partnership Development: The objective is to establish partnerships and collaborations with international counterparts in the field of sustainable development. The Export and Import Offices work to build relationships with sustainable businesses, research institutions, and organizations abroad. These partnerships facilitate the exchange of ideas, best practices, and resources, contributing to the company’s capacity to address global sustainability challenges and leverage international expertise.
5. Compliance with Regulations: The objective is to ensure compliance with international trade regulations and sustainability standards. The Export and Import Offices are responsible for staying updated on import and export regulations, including those related to sustainability, such as certifications and labeling requirements. They work to ensure that the company meets all legal and regulatory obligations in its trade activities while adhering to sustainability criteria.
6. Supply Chain Management: The objective is to manage the sustainability of the company’s supply chain in import and export activities. The Export and Import Offices work closely with suppliers and business partners to assess and enhance the sustainability performance of the supply chain. They encourage suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, monitor compliance with sustainability standards, and address any environmental or social risks associated with the supply chain.
7. Economic Development: The objective is to contribute to sustainable economic development through import and export activities. The Export and Import Offices aim to support local economies and communities by promoting exports of sustainable products, fostering economic growth, and creating employment opportunities. They also explore opportunities for importing sustainable products or raw materials that can contribute to local economic development and promote sustainable livelihoods. By pursuing these objectives, the Export and Import Offices within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company aim to promote sustainable trade practices, expand markets for sustainable products and technologies, facilitate knowledge transfer and partnerships, ensure compliance with regulations, manage supply chain sustainability, and contribute to economic development. These activities align with the company’s commitment to sustainable development and its efforts to integrate sustainability principles into international trade.
Retail Sale via Internet (E-Commerce):
The objectives of engaging in retail sale via the internet (e-commerce) within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Sustainable Product Offering: The objective is to offer a range of sustainable products through e-commerce platforms. The company aims to curate and promote products that align with sustainability principles, such as environmentally friendly, ethically sourced, and socially responsible products. By offering sustainable choices to online consumers, the company encourages responsible consumption and supports the growth of the sustainable product market.
2. Accessibility and Convenience: The objective is to provide convenient access to sustainable products through online retail. E-commerce platforms enable customers to browse and purchase sustainable products from the comfort of their homes, increasing accessibility and convenience. This accessibility helps overcome geographic barriers and encourages a wider audience to adopt sustainable purchasing habits.
3. Environmental Impact Reduction: The objective is to minimize the environmental impact associated with retail operations. E-commerce platforms offer opportunities to optimize logistics, reduce transportation emissions, and implement eco-friendly packaging practices. The company can strive for carbon-neutral shipping, use recyclable materials for packaging, and adopt efficient inventory management systems to minimize waste and energy consumption throughout the supply chain.
4. Consumer Education: The objective is to educate and inform consumers about sustainable choices and practices. The company can utilize e-commerce platforms to provide detailed product descriptions, eco-labeling, and information on the environmental and social impact of products. By educating consumers, the company empowers them to make informed decisions and encourages sustainable consumption patterns.
5. Collaboration with Suppliers: The objective is to collaborate with suppliers to enhance the sustainability of the supply chain. The company can work closely with suppliers to ensure that sustainable practices are followed throughout the production and distribution processes. This collaboration may involve sourcing products from certified sustainable suppliers, promoting fair trade partnerships, and encouraging suppliers to adopt environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
6. Feedback and Engagement: The objective is to engage with customers and gather feedback to improve sustainability efforts. E-commerce platforms provide opportunities for direct communication with customers, allowing the company to collect feedback and suggestions on sustainable product offerings, packaging, and overall shopping experience. This feedback can inform continuous improvement and foster a sense of engagement and co-creation with customers.
7. Measurement and Reporting: The objective is to measure and report on sustainability performance in e-commerce operations. The company can track and report key sustainability metrics, such as carbon emissions, waste reduction, and social impact. Transparent reporting demonstrates the company’s commitment to sustainable practices, fosters accountability, and enables customers to make informed choices based on sustainability performance. By engaging in e-commerce activities with a focus on sustainability, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company aims to offer sustainable product choices, increase accessibility and convenience, reduce environmental impact, educate consumers, collaborate with suppliers, engage with customers, and measure sustainability performance. These objectives contribute to the company’s commitment to sustainable development and its efforts to promote responsible consumption and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
Dental Clinics:
The objectives of operating dental clinics within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Sustainable Healthcare Practices: The objective is to promote sustainable healthcare practices within dental clinics. The company aims to adopt environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices in dental care, such as reducing waste generation, conserving water and energy, using eco-friendly materials and equipment, and implementing proper infection control measures. By integrating sustainability into healthcare operations, the company reduces its ecological footprint and contributes to the overall sustainability of the healthcare sector.
2. Patient Education and Awareness: The objective is to educate and raise awareness among patients about the importance of sustainable oral healthcare. The dental clinics provide information and guidance to patients on sustainable oral hygiene practices, such as water conservation, responsible product use, and proper waste disposal of dental materials. By empowering patients with knowledge, the company promotes individual responsibility and encourages sustainable behavior beyond the clinic setting.
3. Green Infrastructure and Design: The objective is to incorporate sustainable design and infrastructure in dental clinics. The company aims to create dental facilities that are energy efficient, utilize natural lighting, and incorporate eco-friendly materials in construction and furnishings. By implementing green infrastructure, the clinics provide a healthy and sustainable environment for patients and staff while minimizing the ecological impact of the facilities.
4. Waste Management and Recycling: The objective is to implement effective waste management and recycling practices in dental clinics. The company strives to minimize waste generation through proper inventory management and the use of reusable and recyclable materials. It also promotes the separation and recycling of dental waste, such as amalgam separators for mercury-containing materials, to prevent environmental contamination. By managing waste responsibly, the clinics contribute to a circular economy and reduce the environmental burden of healthcare waste.
5. Ethical Sourcing and Responsible Procurement: The objective is to ensure ethical sourcing and responsible procurement of dental equipment, materials, and supplies. The company seeks to partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, adhere to fair labor practices, and offer eco-friendly and socially responsible products. By making conscious procurement decisions, the clinics support sustainable supply chains and contribute to the overall sustainability of the dental industry.
6. Community Health and Engagement: The objective is to promote community health and engagement through dental clinics. The company may organize oral health awareness campaigns, preventive dental care programs, and educational workshops in local communities. By focusing on preventive care and community engagement, the clinics strive to improve oral health outcomes, reduce healthcare disparities, and empower individuals to take an active role in their oral health and overall well-being.
7. Research and Innovation: The objective is to engage in research and innovation to advance sustainable dental practices. The company may conduct research on sustainable oral healthcare technologies, materials, and treatment approaches. It aims to contribute to the scientific knowledge in the field of sustainable dentistry and promote the adoption of innovative and eco-friendly practices in dental clinics worldwide. By operating dental clinics with a focus on sustainability, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company aims to promote sustainable healthcare practices, educate patients, incorporate green infrastructure and design, implement waste management and recycling, ensure ethical sourcing and procurement, engage with communities, and foster research and innovation. These objectives align with the company’s commitment to sustainable development and its efforts to integrate sustainability principles into the healthcare sector for the benefit of patients, communities, and the environment.
Restaurants:
The objectives of operating restaurants within a Sustainable Development Sciences Company are as follows:
1. Sustainable Sourcing of Ingredients: The objective is to prioritize sustainable sourcing of food ingredients for the restaurant’s menu. The company aims to partner with local farmers and suppliers who practice sustainable agriculture, prioritize organic and seasonal produce, and promote fair trade. By sourcing sustainable ingredients, the restaurant supports environmentally friendly farming practices, reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation, and promotes the well-being of local communities.
2. Plant-Based and Healthy Menu Options: The objective is to offer plant-based and healthy menu options that promote sustainable and nutritious diets. The company recognizes the environmental impact of animal agriculture and strives to provide a variety of plant-based dishes that are delicious and satisfying. By promoting plant-based choices, the restaurant contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving resources, and supporting the health and well-being of its customers.
3. Waste Reduction and Recycling: The objective is to implement waste reduction and recycling practices in restaurant operations. The company aims to minimize food waste through proper portioning, inventory management, and donation of surplus food to local charities. It also emphasizes recycling and composting of packaging materials, such as paper, glass, and organic waste. By managing waste responsibly, the restaurant reduces its environmental impact and supports the transition towards a circular economy.
4. Energy Efficiency and Resource Conservation: The objective is to optimize energy efficiency and conserve resources in restaurant facilities. The company implements energy-saving measures, such as LED lighting, efficient kitchen equipment, and smart heating and cooling systems. It also encourages water conservation through the use of low-flow faucets and water-efficient dishwashing practices. By reducing energy consumption and conserving resources, the restaurant minimizes its environmental footprint and contributes to a more sustainable future.
5. Education and Customer Awareness: The objective is to educate customers and raise awareness about sustainable food choices and practices. The restaurant provides information about its sustainability initiatives, such as ingredient sourcing, waste reduction, and energy conservation. It may also organize workshops, cooking classes, or events focused on sustainable eating habits and nutrition. By engaging with customers and promoting awareness, the restaurant encourages informed choices and empowers individuals to make sustainable decisions beyond the dining experience.
6. Collaboration with Local Food Networks: The objective is to collaborate with local food networks and organizations that support sustainable agriculture and food systems. The company may partner with community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, participate in farmers’ markets, or engage in initiatives that connect local producers with restaurants. By fostering relationships with local food networks, the restaurant strengthens the local food economy, supports small-scale farmers, and promotes sustainable and resilient food systems.
7. Continuous Improvement and Innovation: The objective is to continuously improve sustainability practices and foster innovation within the restaurant industry. The company invests in research and development to explore new methods, technologies, and practices that enhance sustainability in restaurant operations. It may experiment with alternative energy sources, explore innovative waste management solutions, or adopt cutting-edge technologies that reduce environmental impact. By embracing innovation, the restaurant contributes to the advancement of sustainable practices in the broader foodservice sector. By operating restaurants with a focus on sustainability, a Sustainable Development Sciences Company aims to promote sustainable sourcing, offer plant-based and healthy menu options, reduce waste and promote recycling, optimize energy efficiency, educate customers, collaborate with local food networks, and drive continuous improvement and innovation. These objectives align with the company’s commitment to sustainable development and its efforts to create a more sustainable and responsible food industry.
Restaurants: acquaintance and cultural development of the nations of the world:
Explaining the objectives of the activity in “Restaurants” in the topic of Sustainable Development Sciences Company:
1. Traditional and Native Sultanate of Oman Foods: The cuisine of Oman is influenced by its Arab, Persian, and Indian heritage. Traditional Omani dishes include Shuwa (marinated lamb cooked in an underground sand oven), Majboos (spiced rice with meat or fish), Mashuai (roasted or grilled spiced fish), Harees (a dish made from ground wheat and meat), and Omani Halwa (a sweet dessert made with rosewater, saffron, and nuts).
2. Traditional and Native Iranian Foods: Iranian cuisine is diverse and reflects the country’s rich history and cultural influences. Popular Iranian dishes include Chelo Kebab (grilled meat served with saffron rice), Ghormeh Sabzi (herb stew with meat), Fesenjan (pomegranate and walnut stew), Tahchin (saffron-infused rice cake with a meat or vegetable filling), and Ash Reshteh (a hearty noodle and bean soup).
3. Traditional and Native Chinese Foods: Chinese cuisine is renowned for its variety and regional specialties. Traditional Chinese dishes include Peking Duck (roast duck served with pancakes and condiments), Kung Pao Chicken (stir-fried chicken with peanuts and vegetables), Dim Sum (steamed or fried bite-sized dumplings and snacks), Mapo Tofu (spicy tofu dish), and Gong Bao Ji Ding (spicy diced chicken with peanuts).
4. Traditional and Native Japanese Foods: Japanese cuisine emphasizes freshness, simplicity, and presentation. Traditional Japanese dishes include Sushi (vinegared rice topped with raw or cooked seafood), Sashimi (thinly sliced raw fish), Tempura (battered and deep-fried seafood and vegetables), Ramen (noodles in a flavorful broth with toppings), and Yakitori (grilled skewered chicken).
5. Traditional and Native South Korean Foods: South Korean cuisine offers a balance of flavors and textures. Traditional South Korean dishes include Kimchi (fermented spicy cabbage), Bibimbap (rice bowl with assorted vegetables and meat), Bulgogi (marinated grilled beef), Japchae (stir-fried glass noodles with vegetables and meat), and Samgyeopsal (grilled pork belly).
6. Traditional and Native Indian Foods: Indian cuisine is known for its vibrant spices and diverse regional dishes. Traditional Indian foods include Biryani (fragrant rice dish with meat or vegetables), Butter Chicken (creamy tomato-based chicken curry), Masala Dosa (fermented rice and lentil crepe with spicy potato filling), Chole Bhature (chickpea curry with fried bread), and Gulab Jamun (deep-fried milk dumplings in syrup).
7. Traditional and Native African Foods: African cuisine varies across the continent, with unique flavors and ingredients. Traditional African dishes include Jollof Rice (spiced rice dish popular in West Africa), Bobotie (South African spiced meat dish with an egg-based topping), Injera (Ethiopian sourdough flatbread), Tagine (slow-cooked stew from North Africa), and Bunny Chow (South African street food with curry served in a hollowed-out loaf of bread).
8. Traditional and Native Australian Foods: Australian cuisine draws inspiration from Indigenous Aboriginal culture and diverse immigrant influences. Traditional Australian foods include Damper (bush bread traditionally cooked in coals), Kangaroo steak (lean meat), Barramundi (Australian fish), Anzac biscuits (oat-based cookies), and Lamingtons (sponge cake coated in chocolate and coconut).
9. Traditional and Native South American Foods: South American cuisine varies by country, with unique ingredients and cooking techniques. Traditional South American dishes include Empanadas (stuffed pastries), Ceviche (marinated raw fish or seafood), Feijoada (Brazilian black bean stew with pork), Asado (Argentinian-style barbecue), and Arepas (cornmeal flatbread typically filled with meat or cheese).
10. Traditional and Native European and American Foods: European and American cuisines encompass a wide range of traditional dishes influenced by various cultures. Traditional European and American foods include Pizza (Italian flatbread topped with various ingredients), Fish and Chips (British battered and fried fish with fries), Steak Frites (French steak with fries), Hamburger (American-style burger with meat patty and toppings), and Apple Pie (classic American dessert).
Restaurants play a crucial role in acquainting people with the cultural development of nations around the world. They serve as culinary ambassadors, offering a taste of traditional and native cuisines from different regions. By experiencing the flavors, ingredients, and cooking techniques of various cultures, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the cultural diversity and development of different nations. Here are some key aspects of how restaurants contribute to cultural development:
1. Culinary Diversity: Restaurants provide a platform for showcasing the culinary diversity of different nations. They offer menus featuring traditional dishes from various regions, allowing people to explore and appreciate the unique flavors, textures, and aromas associated with different cultures. By experiencing these diverse cuisines, individuals can develop a greater appreciation for the cultural heritage and culinary traditions of different nations.
2. Cultural Exchange: Restaurants act as meeting places for people from diverse backgrounds, facilitating cultural exchange. Customers can interact with restaurant staff, who often come from the same cultural backgrounds as the cuisine they serve. This interaction provides an opportunity for cultural dialogue, where customers can learn about the traditions, customs, and stories behind the dishes they enjoy. Through these conversations, individuals can gain insight into the cultural development and practices of different nations.
3. Preservation of Culinary Traditions: Restaurants specializing in traditional and native cuisines play a crucial role in preserving culinary traditions. Many traditional recipes are passed down through generations within families or specific communities. Restaurants that specialize in these cuisines often work closely with culinary experts and local communities to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the dishes they serve. By preserving and promoting traditional recipes, restaurants contribute to the cultural development and heritage of nations.
4. Showcasing Local Ingredients: Restaurants often prioritize sourcing local ingredients, which not only supports local farmers and producers but also highlights the unique flavors and ingredients of a particular region. By incorporating local ingredients into their menus, restaurants showcase the agricultural practices, biodiversity, and natural resources of a specific area. This emphasis on local ingredients contributes to the cultural development and appreciation of a nation’s culinary heritage.
5. Cultural Events and Festivals: Restaurants frequently organize cultural events and festivals that celebrate the traditions and customs of different nations. These events may feature live music, traditional performances, and special menus that highlight specific cultural celebrations or holidays. By immersing customers in the festivities and traditions associated with a particular culture, restaurants contribute to the cultural development and awareness of nations worldwide.
6. Fusion and Innovation: Some restaurants take a creative approach by blending traditional and native cuisines with contemporary techniques and flavors. This fusion of culinary traditions can lead to innovative and exciting dishes that reflect the evolving cultural landscape of a nation. By pushing culinary boundaries and experimenting with new flavors and combinations, these restaurants contribute to the cultural development and evolution of traditional cuisines. In summary, restaurants serve as cultural ambassadors, promoting the cultural development of nations by showcasing traditional and native cuisines, facilitating cultural exchange, preserving culinary traditions, highlighting local ingredients, organizing cultural events, and fostering culinary fusion and innovation. Through these experiences, individuals can deepen their understanding and appreciation of different cultures, contributing to a more interconnected and culturally diverse world.
Best regards,
Professor, Abdolreza Shahrabi Farahani
President/Chief Executive Officer
Sustainable Development Sciences Organization
CEO & President of
Subjective Physics Sciences Organization
Organization Accreditation; Special Consultative Status with the Economic and Social Council of the UN ECOSOC, Since 2023. https://esango.un.org/
Author of the book: Principles of Mechanic Time, based on philosophy: Subjective Physics Sciences and based on the Theory of the Principles of Mechanic Time in the topics (nature of thinking) and (nature, structure and components) of space-time from the perspective of Oriental Sciences and Philosophy.